

We conducted a literature search of MEDLINE (1966-1999) and EMBASE (1988-1999) to identify articles written in English, French, German, or Dutch. We focused on the most common meniscal tests: the assessment of joint effusion, the McMurray test, JLT, and the Apley compression test. (6) Therefore, we systematically reviewed the medical literature to summarize the available evidence about the diagnostic accuracy of physical diagnostic tests for assessing meniscal lesions of the knee and to combine the results of individual studies when possible. (1,2,4) Also, the diagnostic accuracy of the various meniscal tests has been questioned, (3-5) and conflicting results regarding that accuracy have been reported. (1-4) Many meniscal tests, however, are not easy to perform and seem to be prone to errors. Various physical diagnostic tests are available to assess meniscal lesions, such as assessment of joint effusion and joint line tenderness (JLT), the McMurray test, and the Apley compression test. * KEY WORDS Meta-analysis diagnosis physical examination predictive value of tests sensitivity and specificity knee joint knee injuries menisci, tibial. The poor characteristics indicate that these tests are of little value for clinical practice. * CONCLUSIONS The methodologic quality of studies addressing the diagnostic accuracy of meniscal tests was poor, and the results were highly heterogeneous. Only the predictive value of a positive McMurmy test was favorable. The summary receiver operating characteristic curves of the assessment of joint effusion, the McMurray test, and joint line tenderness indicated little discriminative power for these tests.

The study results were highly heterogeneous.
MCMURRAY MENISCUS TEST SENSITIVITY VERIFICATION
The results of the index and reference tests were assessed independently (blindly) of each other in only 2 studies, and in all studies verification bias seemed to be present. * MAIN RESULTS Thirteen studies (of 402) met the inclusion criteria. * DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS Two reviewers independently selected studies, assessed the methodologic quality, and abstracted data using a standardized protocol. * SELECTION CRITERIA Articles written in English, French, German, or Dutch that addressed the accuracy of at least one physical diagnostic test for meniscus injury with arthrotomy, arthroscopy, or magnetic resonance imaging as the gold standard were included. * SEARCH STRATEGY We performed a literature search of MEDLINE (1966-1999) and EMBASE (1988-1999) with additional reference tracking. * OBJECTIVE Our systematic review summarizes the evidence about the accuracy of physical diagnostic tests for assessing meniscal lesions of the knee. * The need for applying advanced diagnostic methods or referral for surgical treatment can be based only on the severity of the patient's complaints.
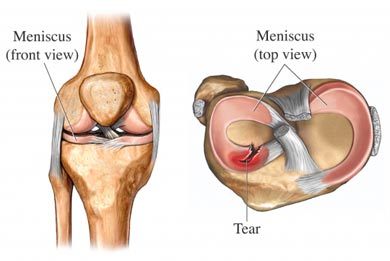
* Physicians should be aware of the limited value of those tests. When the clunk is present, the test has a sensitivity of 98% but, due to the fact that not always is possible to evoke the clunk, its specificity is only 15%.* There is little evidence that the diagnosis of meniscal lesions of the knee can be improved by applying the assessment of joint effusion, the McMurray test, joint line tenderness, or the Apley compression test. The result of the test is considered positive when the patient feels pain in the appropriate joint line accompanied by a thud or click. As a mnemonic rule, the heel of the foot points toward the injured meniscus. As the knee is slowly taken into extension, external rotation stress will test the medial meniscus, whereas internal rotation stress tests the lateral meniscus ( Fig.
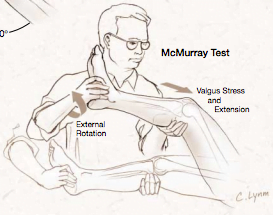
One hand grasps the heel, the knee is steadied, and the joint line palpated with the other hand. The McMurray test is performed with the patient supine, the hip flexed to 90°, and the knee in forced maximal flexion. Also, complementary knee tests may be done in the same position. Special tests for assessing the meniscus, such as the McMurray, Steinmann, and Apley tests, can aid in the diagnosis, but the McMurray test is preferred because it is easy, fast, and reliable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
